最初の例は内積だったが, 今度は外積を使用する.
例: 複素数の外積
マニュアルでは, この例題の単位としてポンドとインチが用いられている. さしあたりそれに従って説明する.
図のような, 長さと角度が $r = 5 \,\mathrm{in} \,\angle 50^{\circ}$ のレバーを考える. このレバーの取っ手部分に $F = 300 \,\mathrm{lb} \cdot \mathrm{in}/\mathrm{s}^2 \,\angle 205^{\circ}$ の力を加えたときのモーメント $M$ を求める.
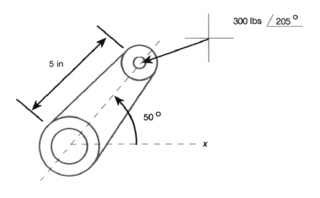
モーメント $M$ は動径ベクトル $r$ と力 $F$ の外積として
\begin{equation*}
\newcommand{\Ar}[1]{\mathrm{Ar}(#1)}
\newcommand{\ar}{\mathrm{ar}}
\newcommand{\arop}{\Opp{\mathrm{ar}}}
\newcommand{\Func}[2]{\mathrm{Func}(#1,#2)}
\newcommand{\Hom}{\mathrm{Hom}}
\newcommand{\Id}[1]{\mathrm{id}_{#1}}
\newcommand{\Mb}[1]{\mathbf{#1}}
\newcommand{\Mr}[1]{\mathrm{#1}}
\newcommand{\Ms}[1]{\mathscr{#1}}
\newcommand{\Ob}[1]{\mathrm{Ob}(#1)}
\newcommand{\Opp}[1]{{#1}^{\mathrm{op}}}
\newcommand{\Pos}{\mathbf{Pos}}
\newcommand{\q}{\hspace{1em}}
\newcommand{\qq}{\hspace{0.5em}}
\newcommand{Rest}[2]{{#1}|{#2}}
\newcommand{\Src}{d^{0,\mathrm{op}}}
\newcommand{\Tgt}{d^{1,\mathrm{op}}}
M = r \times F
\end{equation*} によって求まる. 外積では交換法則は成立しないのでこの順序で計算を行う必要がある.
MODES DEG MODES POLAR ; 度・極座標モードの指定.
5 ENTER 50 COMPLEX ; 動径ベクトル r を複素数として入力.
300 ENTER 205 COMPLEX ; 力ベクトル F を複素数として入力.
MATRIX CROSS ; 外積 r × F を計算.
$\quad \Rightarrow 633.9274 \,[\Mr{lb} \cdot \Mr{in} \cdot \Mr{s}^{-2} \cdot \Mr{in}]$
結果が正の実数なので, モーメントは大きさが約 634 で, 方向が図の面に垂直に上を向いていることになる.
この結果を MKS 単位系に変換すると,
\begin{align*}
633.9274 \,[\Mr{lb} \cdot \Mr{in} \cdot \Mr{s}^{-2} \cdot \Mr{in}]
&= 633.9274 \,[\Mr{lb} \cdot 1/12 \,\Mr{ft} \cdot \Mr{s}^{-2} \cdot 1/12 \,\Mr{ft}] \\
&= 633.9274 \,[0.3732 \,\Mr{kg} \cdot (1/12) \cdot 0.3048 \,\Mr{m} \cdot \Mr{s}^{-2} \cdot (1/12) \cdot 0.3048 \,\Mr{m}] \\
&= 633.9274 \,[2.4077 \cdot 10^{-4} \,\Mr{kg} \cdot \Mr{m} \cdot \Mr{s}^{-2} \cdot \Mr{m}] \\
&= 0.1526 \,[\Mr{N} \cdot \Mr{m}]
\end{align*} となる.
【このカテゴリーの最新記事】
-
no image
-
no image
-
no image
-
no image
-
no image