2018年02月26日
《その310》 sort関数(2)
sort関数 による降順ソート
今回は、sort関数を使って降順ソートを行います。使用する sort関数は、仮引数が3つのバージョンです。
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Compare>
void sort(
RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp
);
降順ソートの際、第3引数には、
(1) <functional>ヘッダが提供する標準ファンクタ greater
(2) greater と同じ bool 値を返却する独自ファンクタ
(3) greater と同じ bool 値を返却する独自関数
(4) greater と同じ bool 値を返却する独自ラムダ式
等を渡すことが可能です。
以下、(1) ~ (4) の4通りを、プログラムで確認します。
(1) のプログラム例
#include <random>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class InputIterator>
void disp(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
for (InputIterator i = first; i != last; i++)
cout << ' ' << *i;
}
int main() {
random_device rd;
vector<int> x;
cout << "◆ベクトルのシャッフルとソート\n";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; i++)
x.push_back(i);
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(x.begin(), x.end(), rd);
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(x.begin(), x.end(), greater<int>());
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "◆通常の配列のシャッフルとソート\n";
char c[] = {
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h'
};
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(c, c + 8, rd);
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(c, c + 8, greater<int>());
disp(c, c + 8); cout << '\n';
}
(2) のプログラム例
#include <random>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
struct f {
bool operator()(T a, T b) {
return a > b;
}
};
template<class InputIterator>
void disp(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
for (InputIterator i = first; i != last; i++)
cout << ' ' << *i;
}
int main() {
random_device rd;
vector<int> x;
cout << "◆ベクトルのシャッフルとソート\n";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; i++)
x.push_back(i);
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(x.begin(), x.end(), rd);
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(x.begin(), x.end(), f<int>());
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "◆通常の配列のシャッフルとソート\n";
char c[] = {
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h'
};
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(c, c + 8, rd);
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(c, c + 8, f<int>());
disp(c, c + 8); cout << '\n';
}
(3) のプログラム例
#include <random>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
bool f(T a, T b) { return a > b; }
template<class InputIterator>
void disp(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
for (InputIterator i = first; i != last; i++)
cout << ' ' << *i;
}
int main() {
random_device rd;
vector<int> x;
cout << "◆ベクトルのシャッフルとソート\n";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; i++)
x.push_back(i);
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(x.begin(), x.end(), rd);
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(x.begin(), x.end(), f<int>);
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "◆通常の配列のシャッフルとソート\n";
char c[] = {
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h'
};
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(c, c + 8, rd);
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(c, c + 8, f<int>);
disp(c, c + 8); cout << '\n';
}
(4) のプログラム例
#include <random>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class InputIterator>
void disp(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
for (InputIterator i = first; i != last; i++)
cout << ' ' << *i;
}
int main() {
random_device rd;
vector<int> x;
cout << "◆ベクトルのシャッフルとソート\n";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; i++)
x.push_back(i);
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(x.begin(), x.end(), rd);
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(x.begin(), x.end(), [](int a, int b) { return a > b; });
disp(x.begin(), x.end()); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "◆通常の配列のシャッフルとソート\n";
char c[] = {
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h'
};
cout << "シャッフル前\n";
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "シャッフル後\n";
shuffle(c, c + 8, rd);
disp(c, c + 8); cout << "\n\n";
cout << "降順ソート後\n";
sort(c, c + 8, [](char a, char b) { return a > b; });
disp(c, c + 8); cout << '\n';
}
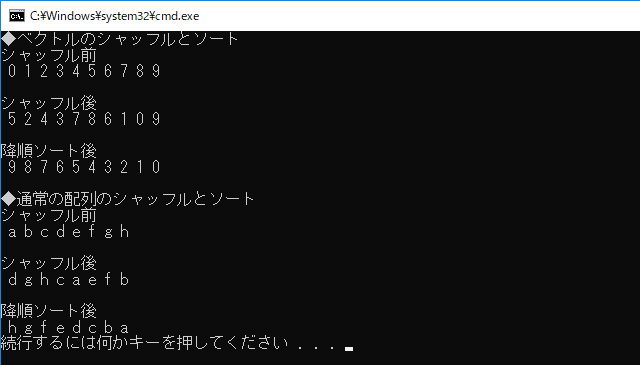
(1) ~ (4) の出力結果は、すべて同じです。
ただし、シャッフルに、擬似乱数ではなく random_device を用いているので、シャッフル後の並びは実行の度に異なります。
この記事へのコメント
コメントを書く
この記事へのトラックバックURL
https://fanblogs.jp/tb/7364957
※ブログオーナーが承認したトラックバックのみ表示されます。
この記事へのトラックバック

