2018年01月19日
《その246》 問題演習 p.325演習9-2
新版明解C++中級編 p.325 演習9-2
本問では、本ブログの《その116》演習1-2 で作成した Date型を利用します。
下記の Twin.h を参考にして、Date型のTwin<> と Twin<> を二値とする Twin<> を作るプログラムを作成せよ。
// Twinヘッダ(Twin.h)
#include <utility>
#include <algorithm>
template <class Type> class Twin {
Type v1;
Type v2;
public:
Twin(const Type& f = Type(), const Type& s = Type())
: v1(f), v2(s) { }
Twin(const Twin<Type>& t)
: v1(t.first()), v2(t.second()) { }
Type first() const { return v1; } // v1 のゲッタ
Type& first() { return v1; } // v1 のゲッタ かつ セッタ
Type second() const { return v2; } // v2 のゲッタ
Type& second() { return v2; } // v2 のゲッタ かつ セッタ
void set(const Type& f, const Type& s) {
v1 = f; v2 = s;
}
Type min() const { return v1 < v2 ? v1 : v2; }
bool ascending() const { return v1 < v2; }
void sort() { if (!(v1 < v2)) std::swap(v1, v2); }
};
template <class Type> inline std::ostream& operator<<(
std::ostream& os, const Twin<Type>& t
) {
return os << "[" << t.first()
<< ", " << t.second() << "]";
}
// 解答
// Date.h
#ifndef ___Class_Date
#define ___Class_Date
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
class Date {
int y;
int m;
int d;
static int dmax[];
static int days_of_year(int year);
static int days_of_month(int year, int month);
public:
static bool leap_year(int year) {
return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
}
Date();
Date(int yy, int mm = 1, int dd = 1);
bool leap_year() const { return leap_year(y); }
int year() const { return y; }
int month() const { return m; }
int day() const { return d; }
Date preceding_day() const;
Date following_day() const;
int day_of_year() const;
int day_of_week() const;
operator long() const;
Date& operator++();
Date operator++(int);
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
Date& operator+=(int dn);
Date& operator-=(int dn);
Date operator+(int dn) const;
Date operator-(int dn) const;
friend Date operator+(int dn, const Date& day);
long operator-(const Date& day) const;
bool operator==(const Date& day) const;
bool operator!=(const Date& day) const;
bool operator> (const Date& day) const;
bool operator>=(const Date& day) const;
bool operator< (const Date& day) const;
bool operator<=(const Date& day) const;
void adjust();
std::string to_string() const;
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, const Date& x);
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& s, Date& x);
#endif
// Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <ctime>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "Date.h"
using namespace std;
int Date::dmax[] = { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int Date::days_of_year(int year) { return 365 + leap_year(year); }
int Date::days_of_month(int year, int month) {
return dmax[month - 1] + (month == 2 && leap_year(year));
}
Date::Date() {
time_t current = time(NULL);
struct tm* local = localtime(¤t);
y = local->tm_year + 1900;
m = local->tm_mon + 1;
d = local->tm_mday;
}
Date::Date(int yy, int mm, int dd) : y(yy), m(mm), d(dd) {
adjust();
}
Date Date::preceding_day() const {
Date temp(*this); return --temp;
}
Date Date::following_day() const {
Date temp(*this); return ++temp;
}
int Date::day_of_year() const { // 該当年内の経過日数
int days = d;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
days += days_of_month(y, i);
return days;
}
int Date::day_of_week() const { // 曜日(0~6)
int yy = y; int mm = m;
if (mm == 1 || mm == 2) { yy--; mm += 12; }
return (yy + yy / 4 - yy / 100 + yy / 400 + (13 * mm + 8) / 5 + d) % 7;
}
Date::operator long() const { // 変換関数(1970/1/1からの日数)
long dys = 0;
for (int i = 1970; i < y; i++)
dys += days_of_year(i);
return dys + day_of_year() - 1;
}
Date& Date::operator++() { // 前置++
return *this += 1;
}
Date Date::operator++(int) { // 後置++
Date temp(*this);
*this += 1;
return temp;
}
Date& Date::operator--() { // 前置--
return *this -= 1;
}
Date Date::operator--(int) { // 後置--
Date temp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return temp;
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int dn) { // 日付を dn日進める。
if (dn < 0)
return *this -= -dn;
d += dn;
adjust();
return *this;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int dn) { // 日付を dn日戻す。
if (dn < 0)
return *this += -dn;
d -= dn;
adjust();
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int dn) const { // dn日後を求める。
Date temp(*this);
return temp += dn;
}
Date Date::operator-(int dn) const { // dn日前を求める。
Date temp(*this);
return temp -= dn;
}
Date operator+(int dn, const Date& day) { // dayのdn日後を求める。
return day + dn;
}
long Date::operator-(const Date& day) const { // 日付の差
return long(*this) - long(day);
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& day) const {
return y == day.y && m == day.m && d == day.d;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& day) const {
return !(*this == day);
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& day) const {
return long(*this) - long(day) > 0 ? true : false;
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& day) const {
return !(*this < day);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& day) const {
return long(*this) - long(day) < 0 ? true : false;
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& day) const {
return !(*this > day);
}
void Date::adjust() {
while (m < 1) { m += 12; y--; }
while (m > 12) { m -= 12; y++; }
while (d < 1) {
if (--m < 1) {
y--; m = 12;
}
d += days_of_month(y, m);
}
while (d > days_of_month(y, m)) {
d -= days_of_month(y, m);
if (++m > 12) {
y++; m = 1;
}
}
if (y < 1970) {
cout << "不正な値が入力されました。\n";
exit(1);
}
}
string Date::to_string() const {
ostringstream s;
s << y << "年" << m << "月" << d << "日";
return s.str();
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& s, const Date& x) {
return s << x.to_string();
}
istream& operator>>(istream& s, Date& x) {
int yy, mm, dd; char c;
s >> yy >> c >> mm >> c >> dd;
x = Date(yy, mm, dd);
return s;
}
// Twin.h
#ifndef ___Class_Twin
#define ___Class_Twin
#include <utility>
#include <algorithm>
template <class Type> class Twin {
Type v1;
Type v2;
public:
Twin(const Type& f = Type(), const Type& s = Type())
: v1(f), v2(s) { }
Twin(const Twin<Type>& t)
: v1(t.first()), v2(t.second()) { }
Type first() const { return v1; } // v2 のゲッタ
Type& first() { return v1; } // v2 のゲッタ かつ セッタ
Type second() const { return v2; } // v2 のゲッタ
Type& second() { return v2; } // v2 のゲッタ かつ セッタ
void set(const Type& f, const Type& s) {
v1 = f; v2 = s;
}
Type min() const { return v1 < v2 ? v1 : v2; }
bool ascending() const { return v1 < v2; }
void sort() { if (!(v1 < v2)) std::swap(v1, v2); }
};
template <class Type> inline std::ostream& operator<<(
std::ostream& os, const Twin<Type>& t
) {
return os << "[" << t.first()
<< ", " << t.second() << "]";
}
#endif
// p325_9_2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Date.h"
#include "Twin.h"
using namespace std;
void input(Date& a, Date& b, Date& c, Date& d) {
cout << "設計開始 : "; cin >> a;
cout << "設計終了 : "; cin >> b;
cout << "生産開始 : "; cin >> c;
cout << "生産終了 : "; cin >> d;
}
double d_m_ratio(Twin<Twin<Date> >& p) {
return
(p.first().second() - p.first().first())
* 1.0
/ (p.second().second() - p.second().first());
}
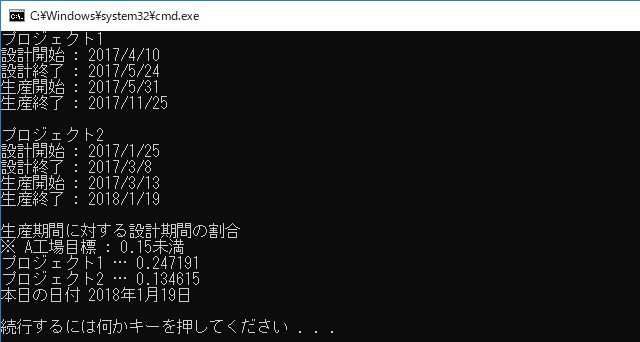
int main() {
typedef Twin<Date> tw;
Date today;
Date s, t, u, v;
cout << "プロジェクト1\n"; input(s, t, u, v);
Twin<tw> project1( tw(s, t), tw(u, v) );
cout << '\n';
cout << "プロジェクト2\n"; input(s, t, u, v);
Twin<tw> project2( tw(s, t), tw(u, v) );
cout << '\n';
cout << "生産期間に対する設計期間の割合\n"
"※ A工場目標 : 0.15未満\n";
cout << "プロジェクト1 … " << d_m_ratio(project1)
<< '\n';
cout << "プロジェクト2 … " << d_m_ratio(project2)
<< '\n';
cout << "本日の日付 " << today << "\n\n";;
}
この記事へのコメント
コメントを書く
この記事へのトラックバックURL
https://fanblogs.jp/tb/7217342
※ブログオーナーが承認したトラックバックのみ表示されます。
この記事へのトラックバック

