2017年10月24日
《その90》 time関数(p.417演習11-6)
time関数
#include <ctime>
time_t time(time_t *timer);
time関数は time_t型の暦時刻を返却します。
time_t型の実体は、unsigned int型やunsigned long型などと同義の算術型。どの型と同義なのかは処理系による。
暦時刻としては、1970年1月1日0時0分0秒からの経過秒数をその値とする処理系が多い。
【time関数の使い方】
time_t型の変数 current で暦時刻を受け取る場合、次のような呼出し方があります。
current = time(NULL);
time(¤t);
current = time(¤t);
新版明解C++入門編 p.417 演習11-6
演習10-1(このブログの《その79》)で作成した人間クラスに誕生日を格納するデータメンバ、それを返却するメンバ関数を追加せよ。
4つのファイル Date.h
Date.cpp
Human.h
HumanTest.cpp
を順に記述します。
// Date.h
#ifndef ___Class_Date
#define ___Class_Date
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
class Date {
int y;
int m;
int d;
public:
Date();
Date(int yy, int mm = 1, int dd = 1);
int year() const { return y; }
int month() const { return m; }
int day() const { return d; }
std::string day_of_week() const;
Date preceding_day() const;
std::string to_string() const;
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, const Date& x);
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& s, Date& x);
#endif
// Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "Date.h"
using namespace std;
Date::Date() {
time_t current = time(NULL);
struct tm* local = localtime(¤t);
/*
↑ tm構造体については、次回《その91》 にチェックする予定です。
*/
y = local->tm_year + 1900;
m = local->tm_mon + 1;
d = local->tm_mday;
}
Date::Date(int yy, int mm, int dd) {
y = yy;
m = mm;
d = dd;
}
string Date::day_of_week() const {
string dw[] = { "日" ,"月", "火", "水", "木", "金", "土" };
int yy = y; int mm = m;
if (mm == 1 || mm == 2) {
yy--;
mm += 12;
}
return dw[(yy + yy / 4 - yy / 100 + yy / 400 + (13 * mm + 8) / 5 + d) % 7];
}
Date Date::preceding_day() const {
int dmax[] = { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
Date temp = *this;
if (temp.d > 1)
temp.d--;
else {
if (--temp.m < 1) {
temp.y--;
temp.m = 12;
}
temp.d = dmax[temp.m - 1];
}
return temp;
}
string Date::to_string() const {
ostringstream s;
s << setfill('0') << y << "年"
<< setw(2) << m << "月"
<< setw(2) << d << "日"
<< "(" << day_of_week() << ")";
return s.str();
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& s, const Date& x) {
return s << x.to_string();
}
istream& operator>>(istream& s, Date& x) {
int y, m, d; char c;
s >> y >> c >> m >> c >> d;
x = Date(y, m, d);
return s;
}
// Human.h
#ifndef ___Class_Human
#define ___Class_Human
#include <string>
#include "Date.h"
class Human {
private:
std::string name; // 氏名
std::string country; // 国籍
double height; // 身長(cm)
double weight; // 体重(kg)
Date birthday; // 誕生日
public:
Human(std::string n, std::string c, double h, double w, const Date& bd)
: name(n), country(c), height(h), weight(w), birthday(bd)
{
}
std::string namae() const { return name; }
Date tanjoubi() const { return birthday; }
std::string kokuseki() const { return country; }
double shinchou() const { return height; }
double taijuu() const { return weight; }
double bmi() const { // 肥満指数BMI
return weight / height / height * 10000;
}
double standard_w() const { // 標準体重(kg)
return height * height * 22 / 10000;
}
};
#endif
// HumanTest.cpp
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Human.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
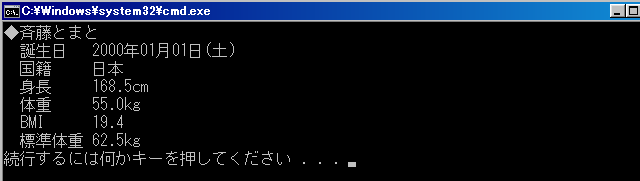
Human saitou("斉藤とまと", "日本", 168.5, 55.0, Date(2000, 1, 1));
cout << "◆" << saitou.namae() << '\n';
cout << " 誕生日 " << saitou.tanjoubi() << '\n';
cout << " 国籍 " << saitou.kokuseki() << '\n';
cout << fixed << setprecision(1);
cout << " 身長 " << saitou.shinchou() << "cm\n";
cout << " 体重 " << saitou.taijuu() << "kg\n";
cout << " BMI " << saitou.bmi() << '\n';
cout << " 標準体重 " << saitou.standard_w() << "kg\n";
}
--
この記事へのコメント
コメントを書く
この記事へのトラックバックURL
https://fanblogs.jp/tb/6892226
※ブログオーナーが承認したトラックバックのみ表示されます。
この記事へのトラックバック


