2018年02月27日
《その312》transformアルゴリズム(1)
transformアルゴリズム
transformアルゴリズムは、コンテナ内の連続する各要素に対して、順番に決められた処理を行い、その結果を別のコンテナに格納します。
transformには、以下に示すように、2つの形式があります。
template <class InputIterator, class OutputIterator, class UnaryOperation>
OutputIterator transform(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
OutputIterator result, UnaryOperation op);
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2,
class OutputIterator, class BinaryOperation>
OutputIterator transform(InputIterator1 first1,
InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2,
OutputIterator result,
BinaryOperation binary_op);
今回のプログラムでは、2番目の形式の transform を使っています。
transform(
a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), c.begin(), plus<int>()
);
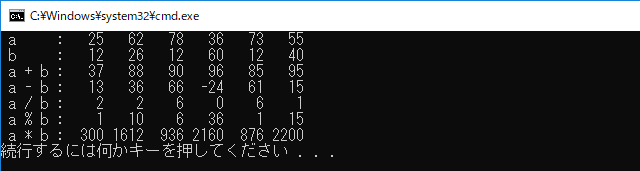
要素 a[0], 要素 b[0] に対して、ファンクタ plus<int>() の処理を行い、その結果を c[0] に格納します。
以下、
a[1], b[1] に対する処理結果を c[1] に格納
a[2], b[2] に対する処理結果を c[2] に格納
a[3], b[3] に対する処理結果を c[3] に格納
・・・・・・・・・・・・
と、a.end() が指す要素まで続けます。
プログラムでは、BinaryOperation binary_op の箇所には、
<functional>ヘッダが提供する、次の算術演算用ファンクタを使っています。
plus
minus
devides
modulus
multiplies
なお、各コンテナの要素の表示には、関数テンプレート for_each を用いました(操作子 setw() で桁数を揃えて出力するファンクタ f を指定)。
for_each(c.begin(), c.end(), f<int>());
関数テンプレート for_each については、本ブログの 《その304》 をご参照ください。
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
struct f : public unary_function<const T&, void> {
void operator()(const T& n) {
cout << setw(5) << n;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> a{ 25, 62, 78, 36, 73, 55 };
vector<int> b{ 12, 26, 12, 60, 12, 40 };
cout << " a :";
for_each(a.begin(), a.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
cout << " b :";
for_each(b.begin(), b.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
vector<int> c(a.size());
transform(
a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), c.begin(),
plus<int>()
);
cout << " a + b :";
for_each(c.begin(), c.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
transform(
a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), c.begin(),
minus<int>()
);
cout << " a - b :";
for_each(c.begin(), c.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
transform(
a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), c.begin(),
divides<int>()
);
cout << " a / b :";
for_each(c.begin(), c.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
transform(
a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), c.begin(),
modulus<int>()
);
cout << " a % b :";
for_each(c.begin(), c.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
transform(
a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), c.begin(),
multiplies<int>()
);
cout << " a * b :";
for_each(c.begin(), c.end(), f<int>());
cout << '\n';
}
この記事へのコメント
コメントを書く
この記事へのトラックバックURL
https://fanblogs.jp/tb/7369794
※ブログオーナーが承認したトラックバックのみ表示されます。
この記事へのトラックバック

