2018年02月10日
《その286》 ベクトル vector<> の基礎事項(6)
ベクトル vector<> の基礎事項(6)
下記のプログラムでは、まず、
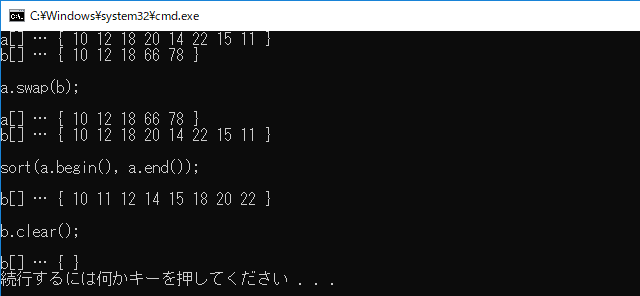
vector<int>型オブジェクト a, b がそれぞれ保持している要素を、メンバ関数 swap を使って、そっくり入れかえます。
a.swap(b);
<algorithm>ヘッダで提供される sort関数を用いて、vector<int>型オブジェクト b の要素を昇順に並べかえることができます。
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
最後に、メンバ関数 clear で、オブジェクト b の全要素を一括削除します。
以下はプログラムです。
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void disp(const vector<int>& x) {
cout << "{ ";
for (vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
cout << x[i] << ' ';
cout << "}";
}
int main() {
int x[] = { 10, 12, 18, 20, 14, 22, 15, 11 };
int y[] = { 10, 12, 18, 66, 78 };
vector<int> a(x, x + sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]));
vector<int> b(y, y + sizeof(y) / sizeof(y[0]));
cout << "a[] … "; disp(a); cout << '\n';
cout << "b[] … "; disp(b); cout << '\n';
cout << "\na.swap(b);\n\n"; a.swap(b);
cout << "a[] … "; disp(a); cout << '\n';
cout << "b[] … "; disp(b); cout << '\n';
cout << "\nsort(a.begin(), a.end());\n\n";
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
cout << "b[] … "; disp(b); cout << '\n';
cout << "\nb.clear();\n\n"; b.clear();
cout << "b[] … "; disp(b); cout << '\n';
}
この記事へのコメント
コメントを書く
この記事へのトラックバックURL
https://fanblogs.jp/tb/7302171
※ブログオーナーが承認したトラックバックのみ表示されます。
この記事へのトラックバック

