新規記事の投稿を行うことで、非表示にすることが可能です。
2020年09月27日
python:matplotlibの覚書:散布図
matplotlibとは
pythonの標準ライブラリでグラフの描画に利用する
matplotlib使い方
よく使うグラフの簡単な使い方を記載しておく。
参考:公式サイトの描画例
幅広い描画方法を記載してあるため、参考になる。
サイトリンク
散布図
基本
matplotlib.pyplot.scatter(x, y, s=None, c=None, marker=None, cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, verts=, edgecolors=None, *, plotnonfinite=False, data=None, **kwargs)
リファレンス- x:float または array
描画するx軸の項目。 - y:float または array
描画するy軸の項目。 - s:float または array
デフォルト値は2。描画するマーカのサイズ。 - c:color または colorリスト
マーカの塗りつぶし色。
描画例
■基本的な描画
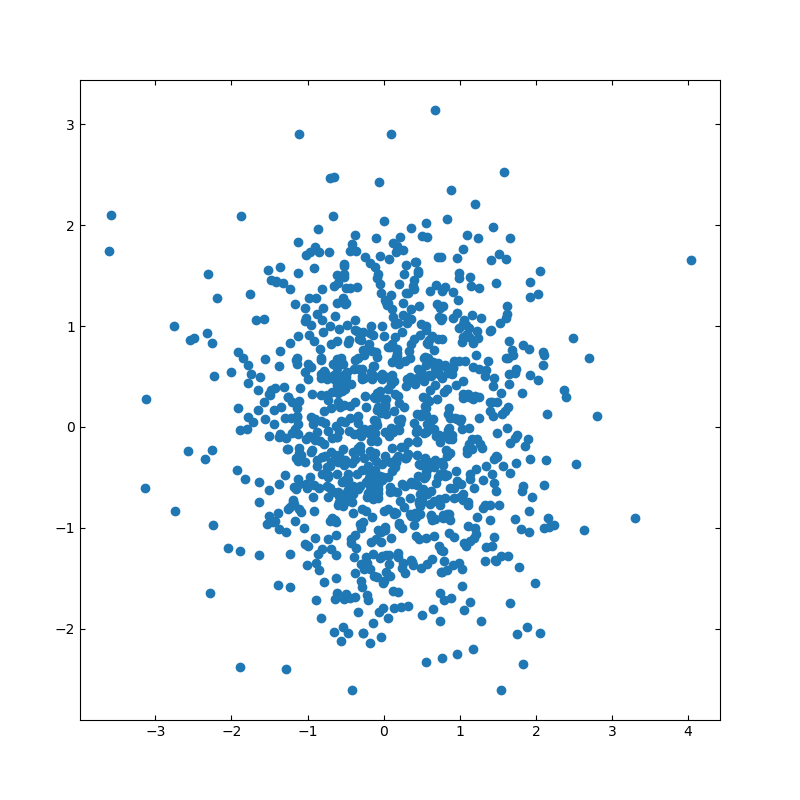
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 散布図のシード値
np.random.seed(19680801)
# 描画用のランダムデータを作成
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
# 軸の設定
left, width = 0.1, 0.8
bottom, height = 0.1, 0.8
spacing = 0.005
rect_scatter = [left, bottom, width, height]
# 描画サイズの設定
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax_scatter = plt.axes(rect_scatter)
ax_scatter.tick_params(direction='in', top=True, right=True)
# 散布図の設定
ax_scatter.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 散布図のシード値
np.random.seed(19680801)
# 描画用のランダムデータを作成
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
# 軸の設定
left, width = 0.1, 0.8
bottom, height = 0.1, 0.8
spacing = 0.005
rect_scatter = [left, bottom, width, height]
# 描画サイズの設定
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax_scatter = plt.axes(rect_scatter)
ax_scatter.tick_params(direction='in', top=True, right=True)
# 散布図の設定
ax_scatter.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
■ヒストグラム付きの散布図
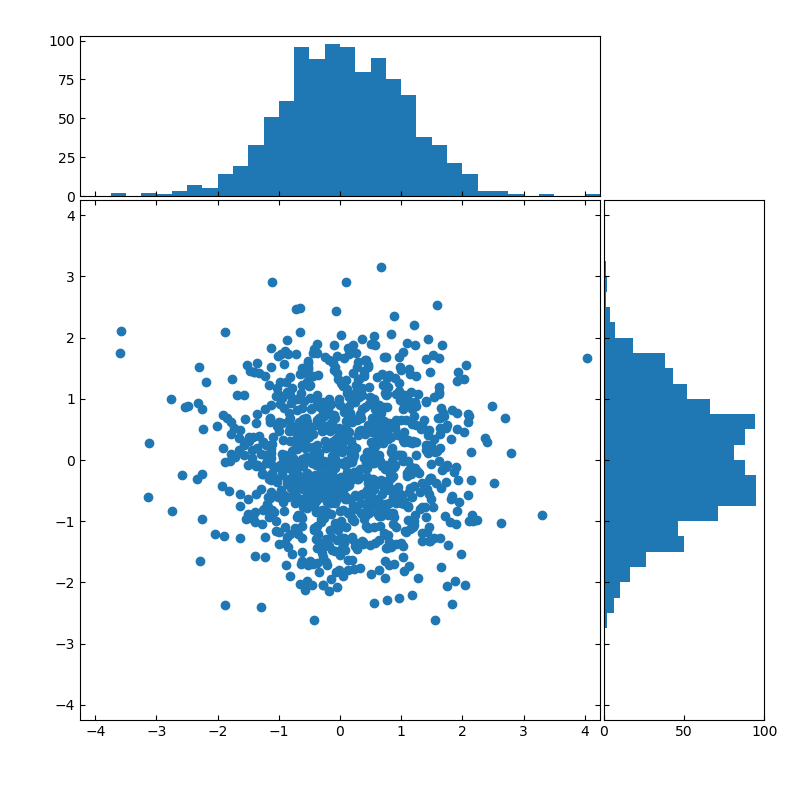
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# the random data
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
# definitions for the axes
left, width = 0.1, 0.65
bottom, height = 0.1, 0.65
spacing = 0.005
rect_scatter = [left, bottom, width, height]
rect_histx = [left, bottom + height + spacing, width, 0.2]
rect_histy = [left + width + spacing, bottom, 0.2, height]
# 描画位置の指定
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax_scatter = plt.axes(rect_scatter)
ax_scatter.tick_params(direction='in', top=True, right=True)
ax_histx = plt.axes(rect_histx)
ax_histx.tick_params(direction='in', labelbottom=False)
ax_histy = plt.axes(rect_histy)
ax_histy.tick_params(direction='in', labelleft=False)
# 描画する散布図データ
ax_scatter.scatter(x, y)
# 描画サイズを指定する
binwidth = 0.25
lim = np.ceil(np.abs([x, y]).max() / binwidth) * binwidth
ax_scatter.set_xlim((-lim, lim))
ax_scatter.set_ylim((-lim, lim))
bins = np.arange(-lim, lim + binwidth, binwidth)
ax_histx.hist(x, bins=bins)
ax_histy.hist(y, bins=bins, orientation='horizontal')
ax_histx.set_xlim(ax_scatter.get_xlim())
ax_histy.set_ylim(ax_scatter.get_ylim())
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# the random data
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
# definitions for the axes
left, width = 0.1, 0.65
bottom, height = 0.1, 0.65
spacing = 0.005
rect_scatter = [left, bottom, width, height]
rect_histx = [left, bottom + height + spacing, width, 0.2]
rect_histy = [left + width + spacing, bottom, 0.2, height]
# 描画位置の指定
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax_scatter = plt.axes(rect_scatter)
ax_scatter.tick_params(direction='in', top=True, right=True)
ax_histx = plt.axes(rect_histx)
ax_histx.tick_params(direction='in', labelbottom=False)
ax_histy = plt.axes(rect_histy)
ax_histy.tick_params(direction='in', labelleft=False)
# 描画する散布図データ
ax_scatter.scatter(x, y)
# 描画サイズを指定する
binwidth = 0.25
lim = np.ceil(np.abs([x, y]).max() / binwidth) * binwidth
ax_scatter.set_xlim((-lim, lim))
ax_scatter.set_ylim((-lim, lim))
bins = np.arange(-lim, lim + binwidth, binwidth)
ax_histx.hist(x, bins=bins)
ax_histy.hist(y, bins=bins, orientation='horizontal')
ax_histx.set_xlim(ax_scatter.get_xlim())
ax_histy.set_ylim(ax_scatter.get_ylim())
plt.show()
2020年09月25日
python:matplotlibの覚書:棒グラフ
matplotlibとは
pythonの標準ライブラリでグラフの描画に利用する
matplotlib使い方
よく使うグラフの簡単な使い方を記載しておく。
参考:公式サイトの描画例
幅広い描画方法を記載してあるため、参考になる。
サイトリンク
棒グラフ
基本
matplotlib.pyplot.bar(x, height, width=0.5, bottom=None, align='center', **kwargs)
リファレンス- x:float または array
棒グラフで描画するx軸の項目。 - height:float または array
各棒グラフの高さ。 - width:float または array
デフォルト値は0.8。各棒グラフの幅。 - bottom:float または array
デフォルト値は0。 - align:['center', 'edge']
デフォルト値は'center'。各棒グラフのボトム(下側)の値 - **kwargs
その他の設定項目。 - color:color または colorリスト
棒グラフの塗りつぶし色 - edgecolor:color または colorリスト
棒グラフの枠色 - xerr, yerr:float または array(形状は(N,)または(2,N)形状。)
誤差分散値
描画例
■基本的な描画
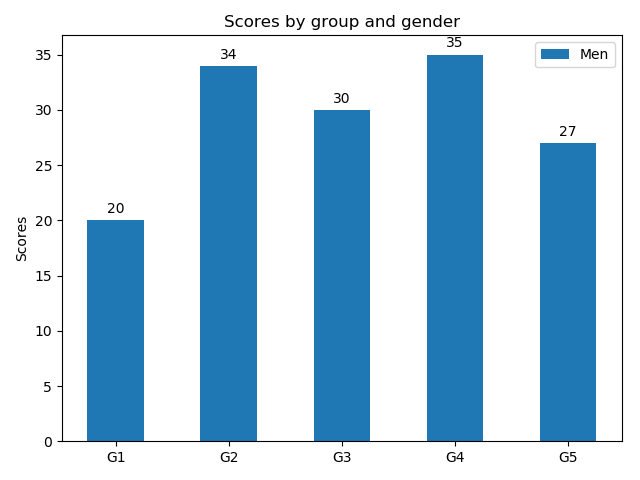
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.5 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.bar(x, men_means, width, label='Men')
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.5 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.bar(x, men_means, width, label='Men')
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
■グループ描画
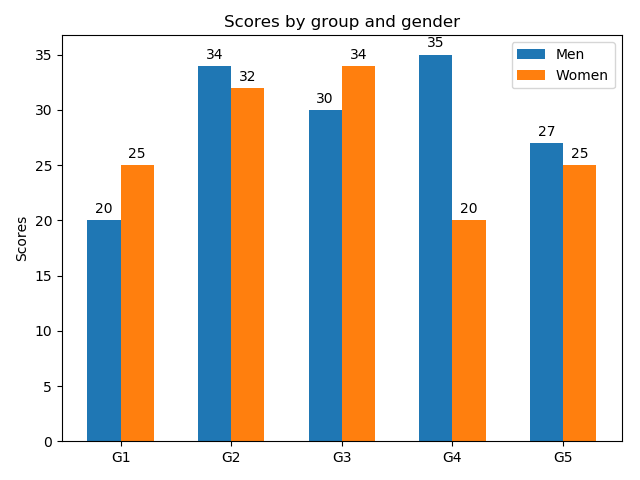
棒グラフの幅を半分にして、横位置をグラフ幅の半分だけ左右にずらして描画している。ずらす量を調整することで、3グループ以上も描画可能。
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
women_means = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.3 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.bar(x - width/2, men_means, width, label='Men')
rects2 = ax.bar(x + width/2, women_means, width, label='Women')
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
women_means = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.3 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.bar(x - width/2, men_means, width, label='Men')
rects2 = ax.bar(x + width/2, women_means, width, label='Women')
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
■積み上げグラフの描画
積み上げる棒グラフの底(bottom)に他方のグラフの高さを設定する。
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
women_means = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.5 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.bar(, men_means, width, label='Men')
rects2 = ax.bar(x, women_means, width, label='Women',bottom=men_means)
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
women_means = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.5 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.bar(, men_means, width, label='Men')
rects2 = ax.bar(x, women_means, width, label='Women',bottom=men_means)
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
■横向きの棒グラフの描画

import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.5 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.barh(x, men_means, width, label='Men')
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_yticks(x)
ax.set_yticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
x = np.arange(len(labels)) # ラベル位置
width = 0.5 # 棒グラフの幅
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects1 = ax.barh(x, men_means, width, label='Men')
# ラベルとタイトルのセット
ax.set_ylabel('Scores')
ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
ax.set_yticks(x)
ax.set_yticklabels(labels)
ax.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()